How Do I Calculate BMI (Body Mass Index)?
How Do I Calculate BMI (Body Mass Index)? Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used tool to assess whether an individual has a healthy body weight for their height.
It is a simple calculation that takes into account a person’s weight and height, and provides a numerical value that falls into different categories, such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
In this article, we will explore the importance of BMI and how to calculate it using pounds and inches. We will also discuss the significance of knowing your BMI and how it can help with weight management and disease prevention.
How to Calculate Your Body Mass Index
Calculating BMI using pounds and inches is relatively straightforward. To calculate your BMI, you need to divide your weight in pounds by your height in inches squared, and then multiply the result by 703.
For example, if you weigh 200 pounds and are 5 feet 6 inches tall (66 inches), the calculation would be as follows:
BMI = (200 / (66^2)) x 703 = 32.3
It is important to note that accurate measurements are crucial for an accurate BMI calculation. Using incorrect measurements can lead to inaccurate results, which may misrepresent an individual’s body weight status.
Understanding BMI: What it is and Why it Matters
BMI is important because it provides a general indication of whether an individual has a healthy body weight for their height. It can be used as a screening tool to identify potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese.
However, it is important to note that BMI is not a direct measure of body fat percentage and does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or distribution of fat.
The Importance of Knowing Your Body Mass Index
Knowing your BMI can have several benefits. Firstly, it can help you understand whether you are at a healthy weight for your height. This information can be useful for setting weight loss or weight gain goals, as well as for monitoring progress towards those goals.
Additionally, knowing your BMI can help you identify potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese. This can prompt you to take action to improve your health and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Interpreting Your BMI Results: What the Numbers Mean
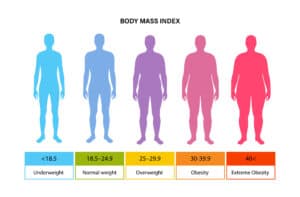
BMI Chart
Body Mass Index results fall into different categories, each indicating a different body weight status. The categories are as follows:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI of 30 or higher
It is important to note that while BMI provides a general indication of body weight status, it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or distribution of fat.
Therefore, it is possible for individuals with a high muscle mass to have a higher BMI, even though they may have a low body fat percentage.
BMI and Health Risks: What You Need to Know
BMI is associated with various health risks. Individuals who are underweight may be at risk of nutrient deficiencies, weakened immune system, and osteoporosis. On the other hand, individuals who are overweight or obese may be at risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Maintaining a healthy BMI is important for overall health. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can reduce their risk of developing these chronic diseases and improve their overall quality of life.
Factors that Affect Your BMI: Age, Gender, and Muscle Mass
Several factors can affect an individual’s BMI, including age, gender, and muscle mass. As individuals age, their metabolism tends to slow down, which can lead to weight gain and an increase in Body Mass Index.
Additionally, men tend to have a higher muscle mass than women, which can result in a higher BMI even if their body fat percentage is low.
It is important to consider these factors when interpreting BMI results. For example, an older individual with a higher BMI may still have a healthy body fat percentage if they have a higher muscle mass. Therefore, it is important to take into account these factors when assessing an individual’s body weight status.
How to Use BMI to Set Realistic Weight Loss Goals

Weight Loss Goals
How Do I Calculate BMI (Body Mass Index)? BMI can be used as a tool to set realistic weight loss goals. By knowing your current BMI and your desired BMI, you can calculate the amount of weight you need to lose to reach your goal. It is important to set achievable goals that are realistic and sustainable in the long term.
For example, if your current BMI is 30 and you want to reach a BMI of 25 (within the normal weight range), you can calculate the weight loss required as follows:
1. Calculate the weight associated with your current BMI:
Weight = (BMI * height^2) / 703
Weight = (30 * (height in inches^2)) / 703
2. Calculate the weight associated with your desired BMI:
Weight = (25 * (height in inches^2)) / 703
3. Subtract the weight associated with your desired BMI from the weight associated with your current BMI to determine the weight loss required.
By setting realistic weight loss goals based on your BMI, you can work towards achieving a healthy body weight and reducing your risk of developing chronic diseases.
The Limitations of BMI: Why it’s Not Always Accurate
While BMI is a useful tool for assessing body weight status, it has its limitations. One of the main limitations is that it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or distribution of fat. This means that individuals with a high muscle mass may have a higher BMI, even though they may have a low body fat percentage.
Additionally, BMI does not differentiate between different types of fat, such as visceral fat (fat around the organs) and subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin). Visceral fat is associated with a higher risk of developing chronic diseases, while subcutaneous fat is less harmful.
Therefore, it is important to consider other factors in addition to BMI when assessing overall health. These factors may include waist circumference, body fat percentage, and blood markers such as cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Other Methods for Measuring Body Fat Percentage
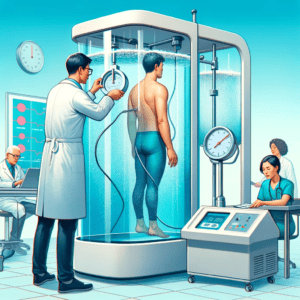
Hydrostatic Weighing
There are several other methods for measuring body fat percentage, which can provide a more accurate assessment of overall health than BMI alone. Some of these methods include:
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA): This method uses X-rays to measure bone density, lean mass, and fat mass.
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA): This method measures the resistance of electrical current as it passes through the body. It can estimate body fat percentage by measuring the amount of resistance encountered by the current.
- Skinfold thickness measurements: This method involves using calipers to measure the thickness of skinfolds at various sites on the body. These measurements are then used to estimate body fat percentage.
- Hydrostatic weighing: This method involves submerging an individual in water and measuring their weight underwater. By comparing their weight underwater to their weight on land, body density can be calculated, which can then be used to estimate body fat percentage.
These methods provide a more accurate assessment of body fat percentage than BMI alone. However, they may not be readily accessible or affordable for everyone.
The Bottom Line: How Do I Calculate BMI (Body Mass Index)?
In conclusion, BMI is a useful tool for assessing body weight status and identifying potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese. By knowing your BMI, you can set realistic weight loss or weight gain goals, monitor progress towards those goals, and take action to improve your overall health.
While BMI has its limitations and does not provide a complete picture of overall health, it is a valuable tool that can be used in conjunction with other measures such as waist circumference, body fat percentage, and blood markers. By considering these factors together, individuals can gain a better understanding of their overall health and take steps to improve it.
It is important to remember that BMI is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to assessing overall health. It should not be used as the sole determinant of health or as a measure of self-worth. Instead, it should be used as a tool to guide individuals towards making positive changes in their lifestyle and improving their overall well-being.