Is Semaglutide The Same As Ozempic?
Is Semaglutide The Same As Ozempic? Semaglutide and Ozempic are both medications that belong to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists.
These medications are used in the management of type 2 diabetes and have been shown to be effective in improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by mimicking the action of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the body.
GLP-1 is released by the intestines in response to food intake and helps regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin secretion, reducing glucagon secretion, and slowing down gastric emptying.
What are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. They work by activating the GLP-1 receptors in the body, which helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Compared to other diabetes medications such as metformin or sulfonylureas, GLP-1 receptor agonists have several advantages. They have been shown to be more effective in lowering blood sugar levels, have a lower risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and can also lead to weight loss.
How do Semaglutide and Ozempic Work?

Ozempic
Semaglutide and Ozempic both work by activating the GLP-1 receptors in the body. This helps regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin secretion, reducing glucagon secretion, and slowing down gastric emptying.
However, there are some differences between Semaglutide and Ozempic in terms of their mechanism of action. Semaglutide is a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist that is administered once weekly, while Ozempic is a once-weekly injection that provides sustained blood sugar control.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
Clinical trials have shown that both Semaglutide and Ozempic are highly effective in improving blood sugar control in patients with type 2 diabetes. In a study called SUSTAIN-6, Semaglutide was shown to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack or stroke compared to placebo.
Similarly, clinical trials for Ozempic have also demonstrated its efficacy in improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. In a study called SUSTAIN-6, Ozempic was shown to significantly reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events compared to placebo.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage for Semaglutide is 0.5 mg once weekly, which can be increased to 1 mg once weekly if additional blood sugar control is needed. Semaglutide is administered as a subcutaneous injection using a prefilled pen.
Ozempic is also administered as a subcutaneous injection using a prefilled pen. The recommended starting dose for Ozempic is 0.25 mg once weekly, which can be increased to 0.5 mg once weekly after four weeks if additional blood sugar control is needed.
Side Effects and Safety Profile
What Are Semaglutide Long-Term Side Effects?
Common side effects of both Semaglutide and Ozempic include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own after a few days or weeks of treatment.
Compared to other diabetes medications such as metformin or sulfonylureas, GLP-1 receptor agonists have a lower risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). However, it is still possible to experience hypoglycemia when taking these medications, especially if they are used in combination with other diabetes medications.
Precautions and Contraindications
Semaglutide and Ozempic should not be used in patients with a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). These medications should also be used with caution in patients with a history of pancreatitis or in patients with severe gastrointestinal disease.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of Semaglutide and Ozempic can vary depending on factors such as insurance coverage and pharmacy discounts. However, in general, these medications can be quite expensive, especially if they are not covered by insurance.
Insurance coverage for Semaglutide and Ozempic can vary depending on the specific insurance plan. Some insurance plans may cover these medications, while others may require prior authorization or have restrictions on their use.
Patient Preferences and Adherence
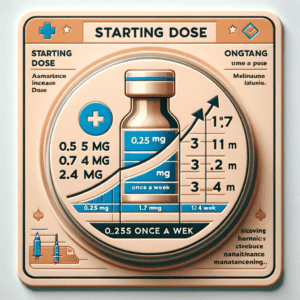
What Is The Best Dosing For Semaglutide?
When choosing between Semaglutide and Ozempic, there are several factors that patients may consider. These factors include the dosing frequency, the method of administration, the cost of the medication, and the potential side effects.
Adherence to medication regimen is crucial for achieving optimal blood sugar control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to discuss these factors with their patients and help them make an informed decision about which medication is best for them.
Comparison of Semaglutide and Ozempic: Similarities and Differences
Semaglutide and Ozempic are both GLP-1 receptor agonists that are used in the management of type 2 diabetes. They have similar mechanisms of action and have been shown to be effective in improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
However, there are some differences between the two medications. Semaglutide is a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist that is administered once weekly, while Ozempic is a once-weekly injection that provides sustained blood sugar control.
Conclusion of Is Semaglutide The Same As Ozempic?
When choosing between Semaglutide and Ozempic, it is important to consider factors such as dosing frequency, method of administration, cost, and potential side effects.
It is also important to consult with a healthcare provider before making a decision, as they can provide guidance based on individual patient needs and preferences. Ultimately, the goal is to find the medication that will best help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.