What Are Semaglutide Long-Term Side Effects?
What Are Semaglutide Long-Term Side Effects? Semaglutide is a medication that is commonly used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, which work by stimulating the release of insulin and reducing the production of glucose in the liver. This helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve glycemic control in individuals with diabetes.
One of the key benefits of Semaglutide is its ability to promote weight loss. Many individuals with type 2 diabetes struggle with obesity, which can further exacerbate their condition. Semaglutide has been shown to help individuals lose weight by suppressing appetite and reducing food intake. In fact, clinical trials have demonstrated that Semaglutide can lead to significant weight loss, with some patients losing up to 15% of their body weight.
In addition to weight loss, Semaglutide also offers other benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It has been shown to improve glycemic control, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, and lower blood pressure. These benefits are crucial in managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications associated with the disease.
The Dark Side of Semaglutide: What You Need to Know
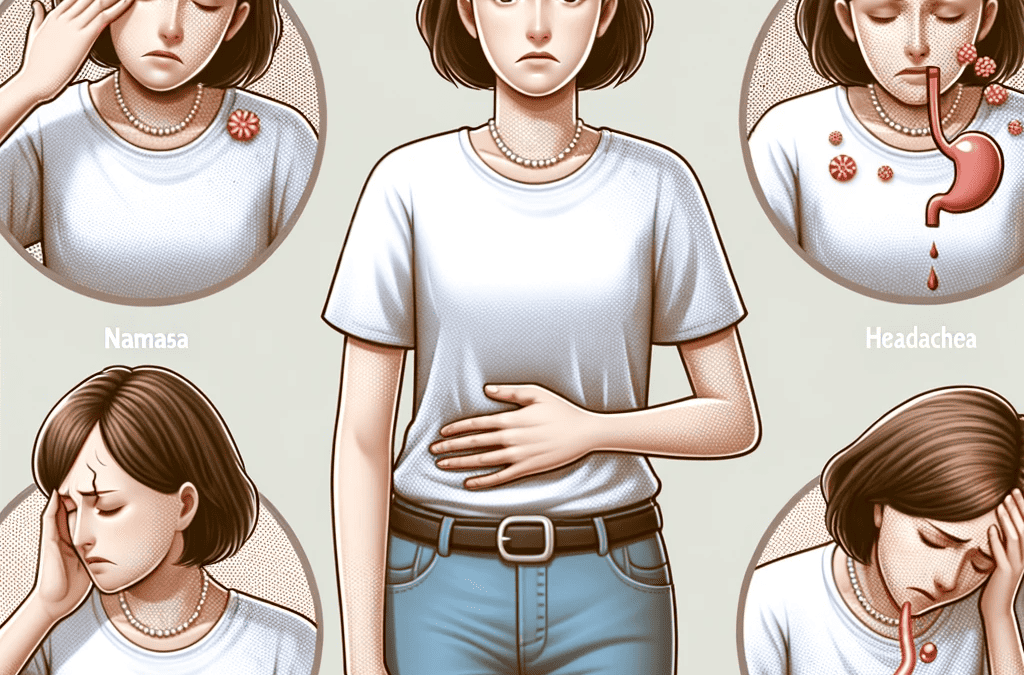
What are semaglutide long-term side effects? While Semaglutide offers numerous benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes, it is important to acknowledge that all medications have potential side effects. Semaglutide is no exception and can have long-term side effects that need to be considered.
It is crucial for individuals considering Semaglutide treatment to be aware of these potential side effects and discuss them with their healthcare provider. While the risks are relatively rare, it is important to weigh the benefits against the potential risks before starting Semaglutide therapy.
Potential Long-Term Side Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide has been associated with several potential long-term side effects. One of the most concerning is the potential risk of cardiovascular events. Some studies have suggested that Semaglutide may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events. However, it is important to note that these studies have been inconclusive, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Semaglutide and cardiovascular risks.
Another potential long-term side effect of Semaglutide is gastrointestinal issues. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects are usually mild and transient, but in some cases, they can be severe and persistent. It is important for individuals taking Semaglutide to report any gastrointestinal symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Semaglutide Use
Several studies have been conducted to investigate the potential cardiovascular risks associated with Semaglutide use. One of the most notable studies is the SUSTAIN-6 trial, which compared Semaglutide to placebo in individuals with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk. The study found that Semaglutide significantly reduced the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke.
However, other studies have suggested a potential increased risk of heart failure with Semaglutide use. The EXSCEL trial found that Semaglutide was associated with a higher rate of hospitalization for heart failure compared to placebo. It is important for individuals with a history of heart failure or other cardiovascular conditions to discuss the potential risks and benefits of Semaglutide with their healthcare provider.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects of Semaglutide
Gastrointestinal side effects are common with Semaglutide use. Nausea is one of the most common side effects reported by individuals taking Semaglutide. It usually occurs during the first few weeks of treatment and tends to improve over time. Other gastrointestinal side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
In most cases, these side effects are mild and transient. However, in some cases, they can be severe and persistent, leading to discontinuation of Semaglutide therapy. It is important for individuals experiencing severe gastrointestinal side effects to consult their healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
Semaglutide and Pancreatitis: What You Need to Know
Pancreatitis
There have been reports of pancreatitis in individuals taking Semaglutide. Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, which can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. While the incidence of pancreatitis with Semaglutide use is rare, it is important for individuals to be aware of this potential risk.
Several studies have investigated the potential link between Semaglutide use and pancreatitis. The LEADER trial, which compared Semaglutide to placebo in individuals with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk, found a slightly higher incidence of pancreatitis in the Semaglutide group compared to the placebo group. However, the overall incidence was low, and the difference was not statistically significant.
Semaglutide and Thyroid Cancer: Is There a Link?
There have been concerns about a potential link between Semaglutide use and thyroid cancer. Some studies have suggested an increased risk of thyroid cancer in individuals taking Semaglutide. However, it is important to note that these studies have been inconclusive, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Semaglutide and thyroid cancer.
The FDA has issued a warning about the potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors with Semaglutide use. C-cell tumors are rare but can be malignant. It is important for individuals taking Semaglutide to be aware of this potential risk and report any symptoms of thyroid cancer, such as a lump in the neck or difficulty swallowing, to their healthcare provider.
Semaglutide and Bone Health: Potential Risks and Concerns
There have been concerns about the potential impact of Semaglutide use on bone health. Some studies have suggested that Semaglutide may increase the risk of fractures and decrease bone mineral density. However, the evidence is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Semaglutide and bone health.
It is important for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or with a history of fractures to discuss the potential risks and benefits of Semaglutide with their healthcare provider. They may need to undergo regular bone density scans and take additional measures to protect their bone health.
Semaglutide and Kidney Function: What You Need to Know
Human Kidneys
What are semaglutide long-term side effects? There have been concerns about the potential impact of Semaglutide use on kidney function. Some studies have suggested that Semaglutide may increase the risk of acute kidney injury and decrease estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). However, the evidence is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Semaglutide and kidney function.
It is important for individuals with pre-existing kidney disease or at risk of kidney disease to discuss the potential risks and benefits of Semaglutide with their healthcare provider. They may need to undergo regular kidney function tests and take additional measures to protect their kidney health.
Conclusion: What Are Semaglutide Long-Term Side Effects?
Semaglutide offers numerous benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced cardiovascular risks. However, it is important to be aware of the potential long-term side effects associated with Semaglutide use.
Individuals considering Semaglutide therapy should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. It is important to weigh the benefits against the potential risks and make an informed decision based on individual needs and circumstances.
Overall, Semaglutide can be a valuable tool in the management of type 2 diabetes, but it is important to be aware of the potential risks and monitor for any signs of adverse effects. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of Semaglutide.